New NSSR Student Group Radically Rethinks Space Exploration
In February 2020, during “those gray days before the pandemic struck,” a new interdisciplinary student group emerged at The New School for Social Research (NSSR). Affectionately nicknamed “Space Squad” or sometimes “that weird space thing,” New School Policy and Design for Outer Space (NS-PDOS) examines the dynamics and distribution of egalitarian models of governance and design in all aspects of space exploration, areas that are frequently overlooked and under-researched in space studies at large. Specific areas of focus include space habitat governance, economy, existential risk, communications & information theory, and bioastronautics.
Asking the Right Questions
The founders of NS-PDOS — Weston Finfer, Rae Rosenthal Boehm, and James Boyd, all NSSR Liberal Studies MA students; Collin McClain, a student in the Bachelor’s Program for Adults and Transfer Students at the Schools for Public Engagement; and Dalia Amellal, from Parsons’ Theories of Urban Practice MA program — met in Post-Planetary Design, an interdisciplinary course at Parsons School of Design taught by Ed Keller, a former Associate Professor. “So many of the questions placed in that class spilled over into everything else we wanted to keep doing,” Finfer says, “so we were like, ‘Let’s keep doing it.’”
One of the fundamental questions that NS-PDOS inherited from Post-Planetary Design is that of scale. How do we think on a microscopic level? Conversely, how do we think on a planetary level? Keller’s September 2020 lecture for NS-PDOS’s launch event, “The Cosmopolitical Gesture — Coordination, Recursivity, and Universal Models,” (embedded below) built on this: “How might we design across a range of different scales and link those design moves and analytical moves back to universalist models?”
NS-PDOS has adopted the strategy from the class of subverting questions to reframe problems of development on Earth and beyond. McClain explains, “One of the things I took from Ed’s class and try to bring to NS-PDOS is using space, using science fiction, and cosmopolitics, to think about geopolitics and think about very earthly issues with a new perspective, but also to consider how we get [beyond Earth], because if we don’t handle issues here on Earth, we can’t get to these eventual futures that we dream of and work towards.” Recalling a class in which Keller coupled footage of burning oil fields with the question “What does oil want?,” Rosenthal Boehm adds that this question, “what does a thing want?” has become her go-to in exploratory conversions, because it ”puts us face-to-face with the limits of our ontological frames and invites us to push beyond them.”
A Social Perspective on Space Exploration
Much of the existing scholarship on space exploration contains thorough design and engineering plans, but doesn’t leave room for error or for the texture of human experience. McClain gives two examples: the assumption that agriculture will thrive as long as we bring the right crops and select out pests, and proposals about governance that do little to address the skewed power dynamic of a governing body controlling the most basic elements of survival —food, water, and even air. Part of NS-PDOS’ work is calling those assumptions into question and seeking radical solutions.
NS-PDOS is a chapter of the international organization “Students for the Exploration and Development of Space (SEDS).” SEDS has historically focused on engineering, technology, and space design, but NS-PDOS brings a different perspective to space exploration by taking social research as their primary mode.
Nick Travaglini, also a Liberal Studies MA student and a core member of the group, says “one of the interesting ways that we try to differentiate ourselves and distinguish ourselves is through making sure that we are very explicitly focused on aspects of the social — coming out of NSSR, we want to make sure social research plays a key role.” In fact, NS-PDOS is at the cutting edge of SEDS’ movement toward incorporating the humanities. The theme of SpaceVision, SEDS’ 2020 international conference, was “Beyond Earth: Humans as an Interplanetary Species.” As part of the conference, Travaglini led a panel discussion called “STEM to STEAM,” about incorporating the arts into space studies.
The conversation brought Travaglini back to questions Keller raised in his NS-PDOS opening lecture: “Suppose we find life in space. How do we think about the dynamics that may play out between humanity and/or other species that we bring into space, away from earth, when we interact with whatever other forms of life may be out there?”
One way to approach these questions, the group proposes, is to take seriously not only hard research, but also speculative writings and films about space, like the 2016 film Arrival. “We need to look at these works and ask, ‘What does this tell us about society now? What does this tell us about changes we can make if we don’t like the speculative futures that may come out of this?’” Travaglini says.
Building a Group in a Pandemic
NS-PDOS’s inaugural meeting — the only time they’ve met in person — was March 10, 2020. Students built NS-PDOS amid a lockdown, working to create relationships and develop a routine. “I know that when I see something coming up in the [NS-PDOS] group chat, it’s going to be something good to discuss this week,” Finfer said. “When we all sign in on Wednesday at 6 PM, we’re going to have a lot to talk about, and that becomes an exciting thing to look forward to.” Over the summer, NS-PDOS members created two working groups, and core membership has grown to 25 students.
The Future Ontologies working group challenges the colonialist and white supremacist thinking that underlies much of the scholarship on space exploration. Rosenthal Boehm, a core member of the group, explains: “In Future Ontologies, we…try to imagine what could we possibly think if we were outside of the moment that we are in, with all known data about failed utopian projects or settlements or outsider projects.”
The group turns to critical theory to unravel a legacy within space studies that includes colonialism, capitalism, and even Nazism. Rosenthal Boehm poses the questions: “If we are living in a community where all of our biometrics are collected by the operating system that runs the community, are we still human? But also, is that fascism? What is the relationship between the technological, the material, the individual and the ideological that plays out in a space habitat that has such radically different terms for existence?”
The Cybernetics and Systems Theory working group looks at the concept of systems broadly, and what it means to think in systems. This overlaps with Finfer’s Liberal Studies MA thesis work on cybernetics, algorithmic information theory, and geoengineering. He has particular interest in the concept of Algorithmic Randomness, a limit in computation that makes absolute certainty impossible.

In addition to the working groups, NS-PDOS also runs the Transceiver Speaker Series, which has, to date, featured Keller, Valerie Olson, and Allison Duettmann. The group is also planning two major events for the Spring 2021 semester:
- A conference on Space Habitats, which will bring together designers, architects, artists, social theorists, and web designers, and which will also include an interactive web-design element that weaves together several space habitats, with attention to detail and consideration for the human experience.
- A conference on Space Laws and Policy. Finfer moderated a panel on the subject at SpaceVision, and hopes this NSSR conference will create a space for more in-depth thought. “ What are the global accords that can help us address planetary scale issues? Our entry into space is such a closed system. It has to be so technically perfect that it doesn’t have room for leaks, errors, entropy, randomness in the same sense that we do on this planet.”
Calling All Space Enthusiasts
NS-PDOS welcomes members from all academic backgrounds and disciplines. Current members includes designers, software engineers, students of Western esotericism and alternative religions, media and culture theorists, and philosophy students. Those interested or curious need not have any background at all in space studies, only need a desire to learn together and an investment in the group’s overall goals.
“We’re interested in bursting open the door to radically new futures,” Rosenthal Boehm says. “Yeah,” adds Finfer. “Basically, we want to change the world.”
For more information or to join NS-PDOS, please visit their website, and follow them on Instagram @newschoolspace and Twitter @nspdos to keep up with upcoming events, like the next installment in the Transceiver Speaker Series.







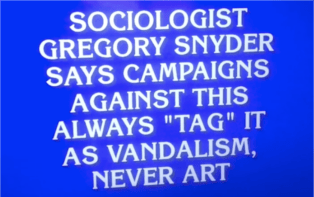 At the time he was first studying it, graffiti had a reputation as more of an urban nuisance than a valuable object of study. “Combating simple binaries is really important,” Snyder suggested. For him, scholarship attains its value precisely acts that complicate—thereby weakening—binary ways of thinking, while at the same time exposing nuance and compelling gray areas. “When things are contradictory, there tends to be beauty involved,” he said. Such was the case with the underground culture of graffiti artists. “To me,” he continued, “graffiti was high art vandalism […] I liked my art vandalistic and my vandalism artistic.”
At the time he was first studying it, graffiti had a reputation as more of an urban nuisance than a valuable object of study. “Combating simple binaries is really important,” Snyder suggested. For him, scholarship attains its value precisely acts that complicate—thereby weakening—binary ways of thinking, while at the same time exposing nuance and compelling gray areas. “When things are contradictory, there tends to be beauty involved,” he said. Such was the case with the underground culture of graffiti artists. “To me,” he continued, “graffiti was high art vandalism […] I liked my art vandalistic and my vandalism artistic.”